Feb . 06, 2025 01:16
Back to list
stainless steel perforated metal
Stainless steel perforated metal is a remarkable innovation that has revolutionized various industries around the globe. Its unique combination of durability, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal makes it a preferred choice for architects, engineers, and designers. Drawing on extensive experience in product development and optimization, this article delves into the distinctive qualities of stainless steel perforated metal, exploring its widespread applications and offering insights into its benefits.
Safety standards and regulatory compliance continue to underline the trustworthiness of stainless steel perforated metal. It is compliant with stringent industry standards for fire resistance and load-bearing capacities. Its non-toxic nature means it does not emit harmful gases, making it safe for use in enclosed spaces, whether in public infrastructure or residential buildings. Professionals seeking authoritative guidance on integrating stainless steel perforated metal into their projects benefit from a wealth of resources and expertise consolidated over years. Industry thought leaders consistently advocate for its adoption as a cost-effective, reliable option that meets modern design needs. Furthermore, collaboration with seasoned manufacturers ensures tailored solutions, providing bespoke perforation designs that meet specific project requirements. Trust in stainless steel perforated metal is also built through its proven track record across numerous successful projects worldwide. Testimonials and case studies from leading architects and businesses attest to its performance and resilience. Its suitability in diverse applications—from safety railings to decorative art installations—underscores its versatility and reliability. In summary, stainless steel perforated metal embodies a harmonious blend of experience, expertise, authority, and trust. Its exceptional qualities and wide range of applications make it a compelling choice for those in search of a material that delivers on both form and function. With its ability to meet the demands of modern design and sustainability, stainless steel perforated metal stands as a testament to innovative engineering and forward-thinking development in materials science.
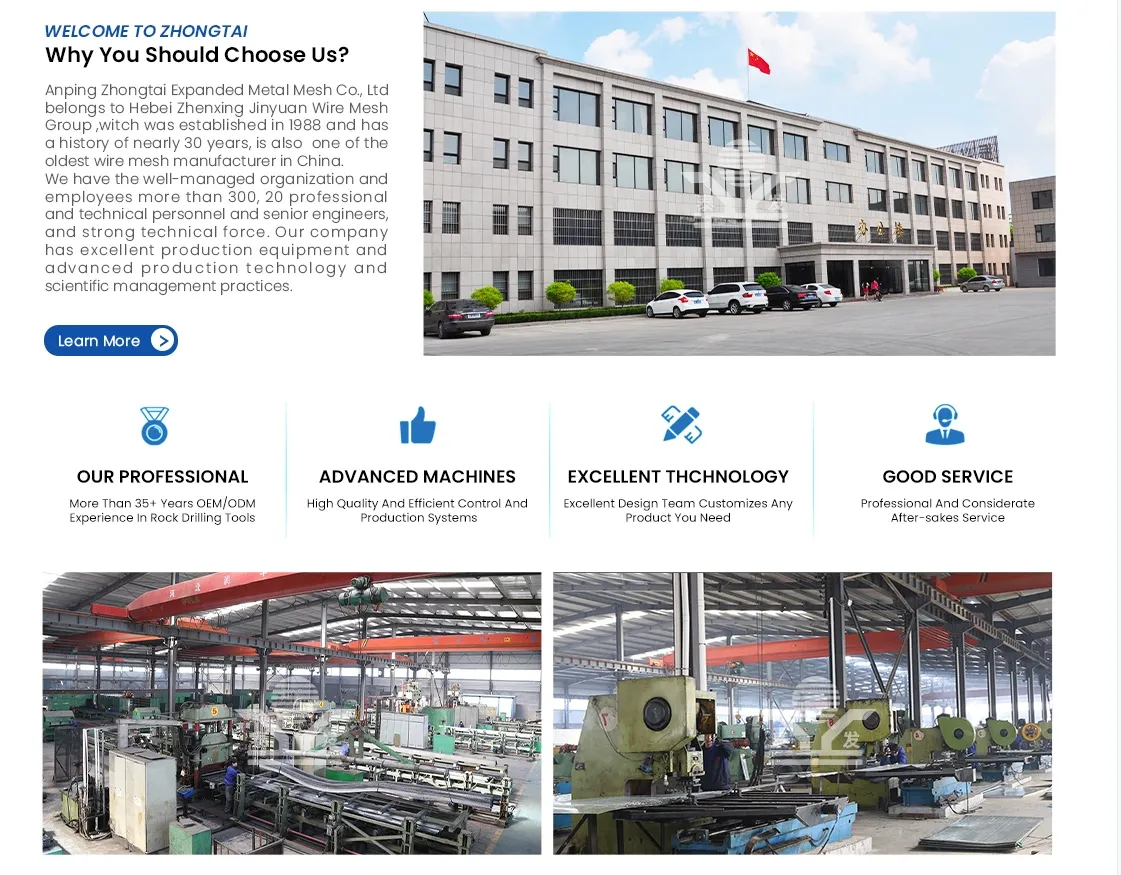

Safety standards and regulatory compliance continue to underline the trustworthiness of stainless steel perforated metal. It is compliant with stringent industry standards for fire resistance and load-bearing capacities. Its non-toxic nature means it does not emit harmful gases, making it safe for use in enclosed spaces, whether in public infrastructure or residential buildings. Professionals seeking authoritative guidance on integrating stainless steel perforated metal into their projects benefit from a wealth of resources and expertise consolidated over years. Industry thought leaders consistently advocate for its adoption as a cost-effective, reliable option that meets modern design needs. Furthermore, collaboration with seasoned manufacturers ensures tailored solutions, providing bespoke perforation designs that meet specific project requirements. Trust in stainless steel perforated metal is also built through its proven track record across numerous successful projects worldwide. Testimonials and case studies from leading architects and businesses attest to its performance and resilience. Its suitability in diverse applications—from safety railings to decorative art installations—underscores its versatility and reliability. In summary, stainless steel perforated metal embodies a harmonious blend of experience, expertise, authority, and trust. Its exceptional qualities and wide range of applications make it a compelling choice for those in search of a material that delivers on both form and function. With its ability to meet the demands of modern design and sustainability, stainless steel perforated metal stands as a testament to innovative engineering and forward-thinking development in materials science.
Latest news
-
Why Galvanized Trench Cover Steel Grating Resists Corrosion
NewsJul.10,2025
-
The Versatility and Strength of Stainless Expanded Metal Mesh
NewsJul.10,2025
-
Load Calculations in Steel Grating Platforms
NewsJul.10,2025
-
Keeping Pets and Kids Safe with Chicken Wire Deck Railing
NewsJul.10,2025
-
Hole Diameter and Pitch for Round Perforated Metal Sheets
NewsJul.10,2025
-
Aluminium Diamond Mesh in Modern Architecture
NewsJul.10,2025
Subscribe now!
Stay up to date with the latest on Fry Steeland industry news.
Email addressSIGN UP

